- +86 152 1709 1354
- [email protected]
- Dongguan,China
- Blog
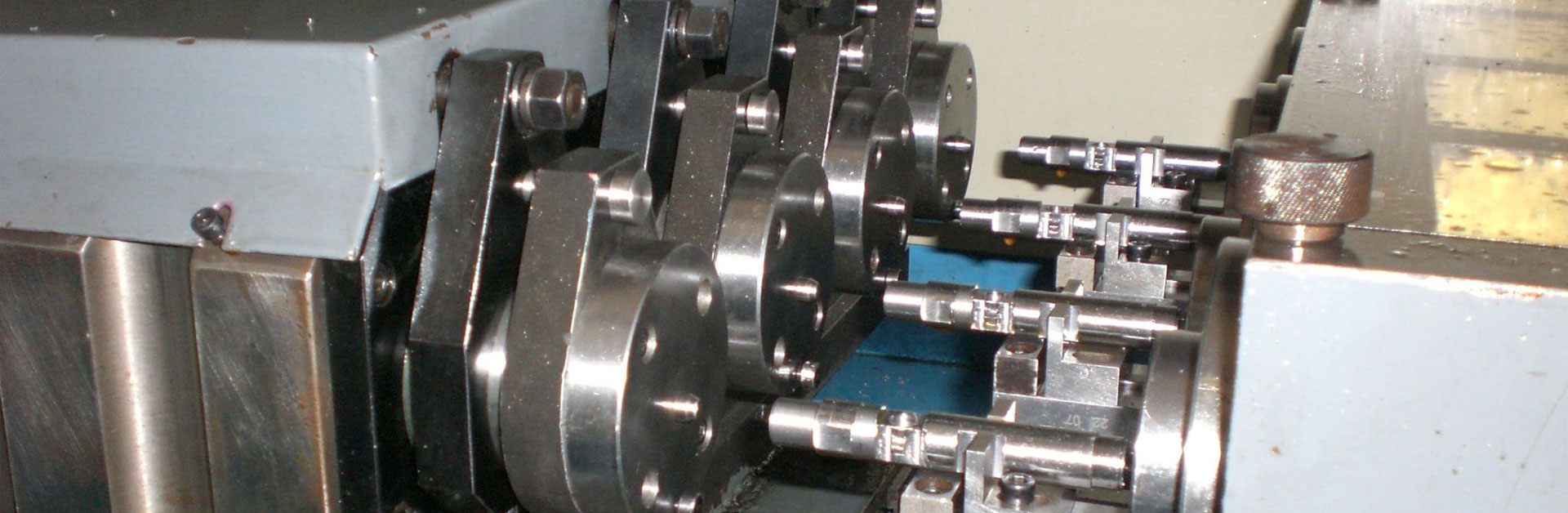
– Cnc Turning Definition
CNC turning is a method of cutting a workpiece by turning the workpiece relative to the tool on a lathe. The cutting energy of turning is mainly provided by the workpiece rather than the tool. Turning is the most basic and common cutting method, and it occupies a very important position in production. Turning is suitable for machining rotating surfaces. Most of the workpieces with rotating surfaces can be processed by turning methods, such as inner and outer cylindrical surfaces, inner and outer conical surfaces, end surfaces, grooves, threads and rotating forming surfaces. The tools used are mainly turning tools. Among various types of metal cutting machine tools, lathes are the most widely used, accounting for about 50% of the total number of machine tools. The lathe can be used for turning of workpieces with turning tools, as well as drilling, reaming, tapping and knurling operations with drills, reamers, taps and knurling tools. According to different process characteristics, layout forms and structural characteristics, lathes can be divided into horizontal lathes, floor lathes, vertical lathes, turret lathes and profiled lathes.
– Technical Problem
Turning machining is the most widely used in the machine manufacturing industry. The number of lathes is large, the number of staff is large, the machining range is wide, and the tools and fixtures used are numerous. Therefore, the safety technical issues of turning machining are particularly important , Its key work is as follows: 1. The damage and protective measures of cutting chips. The various steel parts processed on the lathe have good toughness, the chips generated during turning are rich in plastic curling, and the edges are relatively sharp. When cutting steel parts at high speed, red hot and long chips will be formed, which is very easy to hurt. At the same time, it is often wrapped around the workpiece, turning tool and tool holder. It should be cleared when stopping, but it is absolutely forbidden to clear or pull off by hand. In order to prevent chip damage, measures such as chip breaking, chip flow control and various protective baffles are often adopted. The measure of chip breaking is to grind the chip breaking groove or step on the turning tool; adopt the appropriate chip breaker and use the mechanical clamping tool. 2. Workpiece clamping. In the process of turning, there are many accidents that damage the machine tool, break or break the tool, and the workpiece falls or flew out and hurts due to improper workpiece clamping. Therefore, in order to ensure the safe production of turning, special care must be taken when loading workpieces. Appropriate fixtures should be used for parts of different sizes and shapes, regardless of the connection between the three-jaw, four-jaw chucks or special clamps and the spindle must be stable and reliable. The workpiece should be clamped and clamped, and the large workpiece can be clamped with a sleeve to ensure that the workpiece does not shift, fall off or throw out when the workpiece rotates at high speed and the cutting force is applied. If necessary, it can be strengthened and fixed with the top and center frame. Immediately after tightening, remove the moving hand. 3. Safe operation. Check the machine tool thoroughly before work to confirm that it is good before use. The clamping of the workpiece and the tool ensures the correct position, firmness and reliability. During the process, when changing the tool, loading and unloading the workpiece and measuring the workpiece, you must stop. When the workpiece is rotating, it must not be touched by hand or wiped with cotton thread. Appropriate selection of cutting speed, feed rate and strenuous depth is not allowed to overload machining. Workpieces, work fixtures and other debris shall not be placed on the head of the bed, the knife holder and the bed surface. When using the file, move the turning tool to a safe position, with the right hand in front and the left hand in the back to prevent the sleeves from getting involved. The machine tool shall be used and maintained by a special person, and no other personnel shall use it.
– Cnc Turning Precautions
The process of CNC lathe machining is similar to that of ordinary lathes, but since CNC lathes are clamped once, all automatic turning processes are completed automatically. Therefore, the following aspects should be noted. 1. Reasonable choice of cutting amount For high-efficiency metal cutting, the material to be processed, cutting tools, and cutting conditions are the three major elements. These determine the machining time, tool life and machining quality. The cost-effective machining method must be a reasonable choice of cutting conditions. The three elements of cutting conditions: cutting speed, feed and cutting depth directly cause tool damage. As the cutting speed increases, the tool tip temperature will rise, and mechanical, chemical, and thermal wear will occur. Cutting speed increased by 20%, tool life will be reduced by 1/2. The relationship between the feed conditions and the wear on the back of the tool occurs within a very small range. However, the feed rate is large, the cutting temperature rises, and the rear wear is large. It has less influence on the tool than the cutting speed. Although the depth of cut has no influence on the cutting speed and feed rate, when cutting at a small depth of cut, the hardened layer of the material to be cut will also affect the life of the tool. The user should select the cutting speed to be used according to the processed material, hardness, cutting status, material type, feed rate, cutting depth, etc. The selection of the most suitable machining conditions is selected on the basis of these factors. Regular and stable wear and tear to reach the life is the ideal condition. However, in actual operations, the choice of tool life is related to tool wear, dimensional changes to be processed, surface quality, cutting noise, machining heat, etc. When determining the machining conditions, it is necessary to study according to the actual situation. For hard-to-machine materials such as stainless steel and heat-resistant alloys, coolant or rigid blades can be used. 2. Reasonable tool selection
- (1) When rough turning, choose a tool with high strength and good durability, so as to meet the requirements of large back eating amount and large feed during rough turning.
- (2) When finishing, choose a tool with high accuracy and good durability to ensure the requirements of machining accuracy.
- (3) In order to reduce the tool change time and facilitate tool setting, the machine clamp knife and machine clamp blade should be used as much as possible.
3. Reasonable choice of fixture
- (1) Try to use a general fixture to clamp the workpiece, and avoid using a special fixture;
- (2) The positioning benchmarks of the parts overlap to reduce positioning errors.
4. Determine the machining route The machining route is the movement path and direction of the tool relative to the part during the machining of the index-controlled machine tool.
- (1) It should be able to ensure the machining accuracy and surface roughness requirements;
- (2) The machining route should be shortened as much as possible to reduce the tool empty travel time.
5. The relationship between machining route and machining allowance At present, under the condition that the CNC lathe has not yet reached the universal use, the excess allowance on the blank should be generally arranged on the ordinary lathe for machining. If you must use a CNC lathe for machining, you need to pay attention to the flexible arrangement of the program. 6. Main points of fixture installation At present, the connection between the hydraulic chuck and the hydraulic clamping oil cylinder is achieved by the * pull rod. The main points of the hydraulic chuck clamping are as follows: first, remove the nut on the hydraulic oil cylinder with a hand, remove the pull tube, and pull it out from the rear end of the spindle, then The chuck can be removed by removing the chuck fixing screw with a carrying hand.
– General process code for turning
Clamping Of Turning Tools
1) The turning tool bar should not extend too long, and the general length should not exceed 1.5 times the height of the tool bar (except for hole, groove, etc.) 2) The center line of the turning tool bar should be perpendicular or parallel to the direction of the tool. 3) Adjustment of the tip height:
- (1) When turning the end face, turning cone surface, turning thread, turning forming surface and cutting solid workpiece, the tool tip should generally be the same height as the workpiece axis.
- (2) The outer circle of rough turning, fine turning hole and tool tip should be slightly higher than the axis of the workpiece.
- (3) When turning thin and long shafts, thick turning holes, and cutting hollow workpieces, the tip should generally be slightly lower than the axis of the workpiece.
4) The bisector of the tip angle of the thread turning tool should be perpendicular to the axis of the workpiece. 5) When clamping the turning tool, the shims under the shank should be small and flat, and the screws pressing the turning tool should be tightened.
Workpiece clamping
- 1) When the workpiece is clamped by a three-jaw self-centering chuck for rough turning or fine turning, if the diameter of the workpiece is less than 30 mm, its overhang should be no more than 5 times the diameter, and if the diameter of the workpiece is above 30 mm, its overhang The length should not be greater than 3 times the diameter.
- 2) When clamping irregular workpieces with four-jaw single-action chucks, faceplates, angle irons (bent plates), etc., the counterweight must be added.
- 3) When machining shaft-type workpieces between centers, the axis of the tailstock center should be adjusted to coincide with the axis of the lathe spindle before turning.
- 4) When machining the slender shaft between the two centers, the follow tool holder or the center holder should be used. In the process of machining, pay attention to adjust the top center’s top tension, and pay attention to the lubrication of the dead center and the center frame.
- 5) When using the tailstock, the sleeve should extend as short as possible to reduce vibration.
- 6) When clamping a workpiece with a small supporting surface and a high height on the vertical lathe, you should use a heightened jaw, and add a lever or a pressure plate to press the workpiece at the appropriate position.
- 7) When turning castings and forgings of wheels and sleeves, the unprocessed surface should be aligned to ensure uniform wall thickness after machining.
Turning Machining
- 1) When turning the stepped shaft, in order to ensure the rigidity when turning, generally the larger diameter part should be turned first, and then the smaller diameter part should be turned.
- 2) When grooving the workpiece on the shaft, it should be done before finishing to prevent the workpiece from deforming.
- 3) When turning a threaded shaft, you should finish turning the unthreaded part after threading.
- 4) Before drilling, flatten the end face of the workpiece. If necessary, the center hole should be punched first.
- 5) When drilling deep holes, generally drill pilot holes first.
- 6) When turning holes of (Φ10—Φ20)㎜, the diameter of the shank should be 0.6-0.7 times the hole diameter to be processed; when machining holes with a diameter greater than Φ20㎜, the shank of the clamping head should generally be used.
- 7) When turning multi-start threads or multi-start worms, perform trial cutting after adjusting the exchange gear.
- 8) When using an automatic lathe, adjust the relative position of the tool and the workpiece according to the adjustment card of the machine tool, and perform trial turning after the adjustment. The first piece can be processed only after passing the test; pay attention to the wear of the tool and the size and surface of the workpiece at any time during the machining degree.
- 9) When turning on a vertical lathe, after the tool holder is adjusted, the beam cannot be moved at will.
- 10) When the relevant surface of the workpiece has position tolerance requirements, try to complete the turning in one clamping.
- 11) When turning the cylindrical gear tooth blank, the hole and the reference end face must be processed in one clamping. If necessary, the marking line should be drawn near the gear dividing circle on the end surface.
12 small experiences in CNC machining
At present, many domestic CNC machine tool operators are classified as follows: some operators are very familiar with mechanical processing, ...
Read More →
Selection of parting surface of die casting mold
In order to remove the blank from the die casting mold, the mold needs to be properly divided into several ...
Read More →
What is sheet metal?
Sheet metal is a metal product processing technology, and there is no complete definition of sheet metal so far.According to ...
Read More →
Where is the road to CNC machining development?
A few days ago, PTJ Engineering issued a document saying that it “processed CNC low-cost orders.” This will hurt yourself ...
Read More →
Skillful use of 4 types of CNC Machining technology
First, the undercut knife method Outer convex processingAs shown in FIG. 1, when the outer opening is projected outward, the ...
Read More →
Stainless steel UG crankshaft CNC machining technology
The crankshaft is the center of the internal combustion engine and the core of the engine. If the function cannot ...
Read More →
Table of Contents
Our service
- Cnc Machining
- Swiss Turning
- Swiss Machining
- 5 Axis Machining
- Precision Turning
- Swiss Screw Machining
- Turn-Mill Machining
